Modeling Online Belief Landscapes
Various forces influence how people update their beliefs. One of these is a tendency to place more credibility in information that is consistent with what we already know and believe. This force is a cognitive force, and is an aggregate of several cognitive phenomena, including cognitive dissonance and confirmation bias. Another important force comes from our social relations. Again, this social force is described by several social psychological constructs, including social influence and social identity theory.
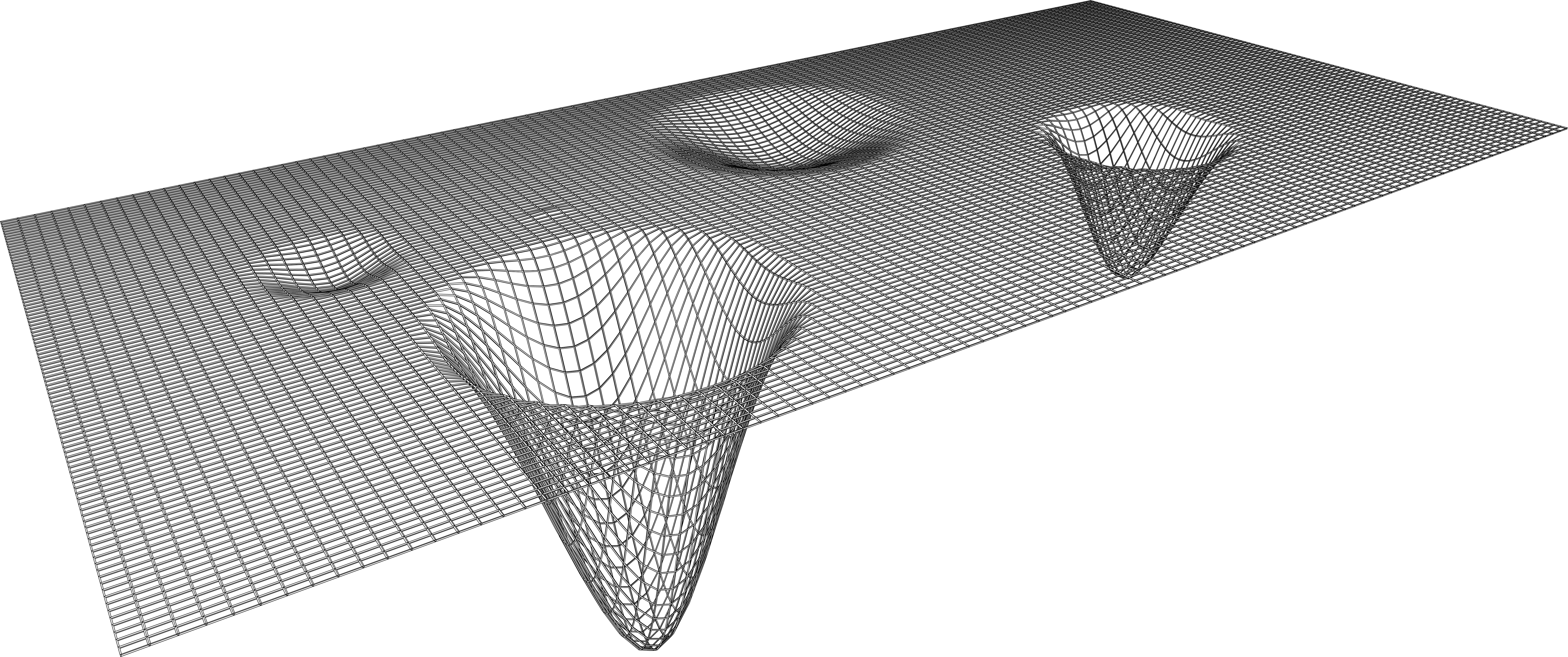
We have developed a framework for exploring how these two forces interact to guide the evolution of beliefs amongst groups of people. Inspired by Stuart Kauffman’s use of the term fitness landscape, we call our framework the belief landscape framework (BLF). As with a fitness landscape, the belief landscape can be imagined as a surface where some points are more ‘optimal’ than other—either peaks or valleys depending on your perspective (we think of them as valleys). In our case, more optimal points describe more coherent1 systems of belief. In other words, the topology of the landscape is driven by the cognitive forces described above.
In the absence of other forces, the BLF predicts that people will tend drift across the belief landscape and congregate in valleys. More will flow into the larger valleys, and they will stay longer in the deepest regions. However, the movement of people across the belief landscape is also heavily influenced by social forces. Whereas the landscape itself may be relatively static, social forces are dynamic. As a result the manner in which the population moves across this landscape is quite complex.
We use the BLF to investigate a series of questions, including:
- What is the structure of the belief landscape, and can we use it to predict individual’s likely future belief states?
- How does social technology influence the dynamics of collective beliefs online?
- Do people in different regions of a belief space exhibit different information behaviors (e.g. sharing misinformation)?
- What governs the logic of coherence?
We are currently exploring these questions in a set of subprojects, that include modeling belief landscapes on Reddit and Twitter, detecting inflection points in individual belief change, and exploring different assumptions within the model using agent-based modeling.
1Our interpretation of coherence is better aligned with Fisher’s notion of narrative coherence and Lombrozo’s interpretation of explanatory preferences (PDF) and rather than logical consistency.